FBOY Island stars Nakia Renee, CJ Franco, and Sarah Emig, three women who are searching for love in an ocean full of Fboys There are 24 men, 12Perform the GaussJordan elimination (reduce completely) of $$$ \left\begin{array}{ccc}1 & 3 & 14\\7 & 1 & 10\end{array}\right $$$ Solution Subtract row $$$ 1 $$$ multiplied by $$$ 7 $$$ from row $$$ 2 $$$ $$$ R_{2} = R_{2} 7 R_{1} $$$Play this game to review Other Solve the system x 6y = 17 x 3y = 8

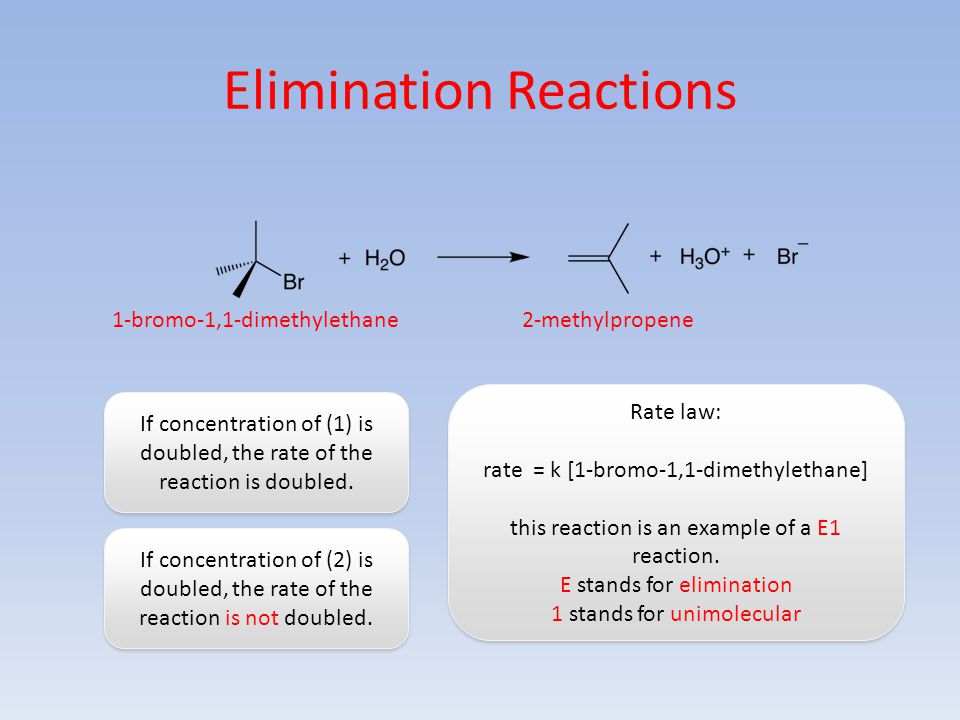
Elimination Reactions Chapter 6 1 Elimination Reactions W
1 elimination 1 piece of clothing
1 elimination 1 piece of clothing-Eliminationsystemofequationscalculator en Related Symbolab blog posts High School Math Solutions – Systems of Equations Calculator, Elimination A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations with the same set of variables In this blog post,GaussJordan elimination More Examples Example 124 Example 124 Example Use the method of Gaussian elimination to solve the system (6), using analogous steps Recall the system 8 >> < >> x 1 3 4 = 4 Eqn 1 6x 2 3x 3 3x 4 = 0 Eqn 2 3x 2 2 4 = 1 Eqn 2x 1 x 2 4x 3 = 5 Eqn 4 (7) Satya Mandal, KU Chapter 1 System of Linear Equations x 12



1 1 Elimination Chemistry Libretexts
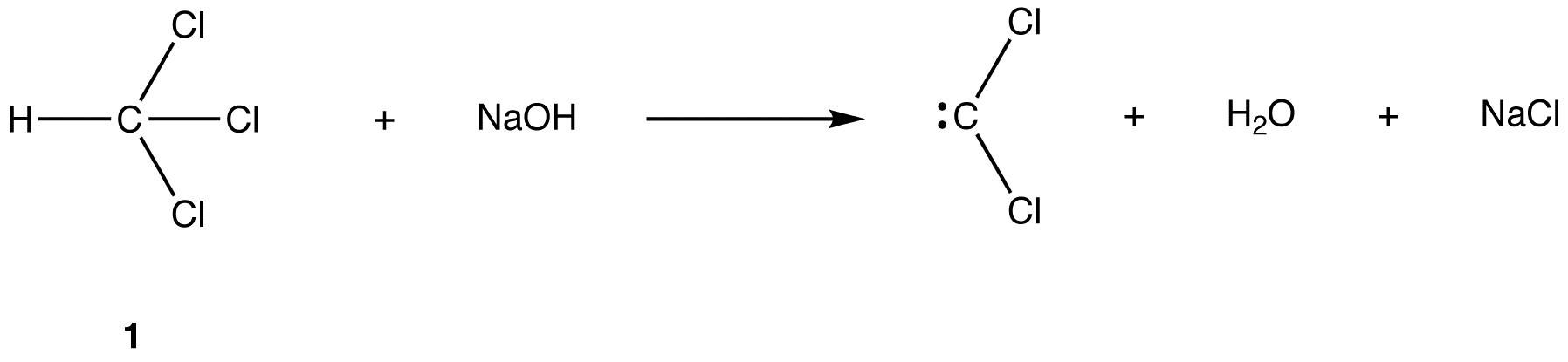
1 a ij R i 7!R i, (ii)For each integer k > i, R ik a ik;jR i 7!R ik Said more simply, make the nonzero entry a ij into a 1, and use this 1 to eliminate (make 0) all other entries directly below the (i;j)th entry A Havens The GaussJordan Elimination Algorithm Drug elimination is the sum of the processes of removing an administered drug from the body In the pharmacokinetic ADME scheme (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) it is frequently considered to encompass both metabolism and excretion Hydrophobic drugs, to be excreted, must undergo metabolic modification making them more polarA 1,1elimination or αelimination is an elimination reaction in which an organic compound loses two ligands from the same atom eg net reaction In this elimination reaction, the two ligands 1 loses, H and Cl, are on the same atom Therefore, this elimination reaction is a 1,1elimination reaction see also 1,2elimination
Thus, we have successfully designed PEG conjugated specifiers or "triggers" as part of a doubleprodrug strategy that relies, first, on enzymatic separation of PEG followed by the classical and rapid 1,4 or 1, 6benzyl elimination reaction releasing the 1 A , C 2 B, B 3 4 False They can be thermodynamically controlled to favor a certain product over another 5 By definition, an E1 reaction is a Unimolecular Elimination reaction This means the only rate determining step is that of theGaussian elimination with partial pivoting 151 The Algorithm We illustrate this method by means of an example Example 1 x 1 x 2 3x 3 = 13 (1) 4x 1 2x 2 x 3 = 15 or 3x 1 x 2 4x 3 = 8 or Ax = b where A = 1 3 1 4 and b = 13 15 8
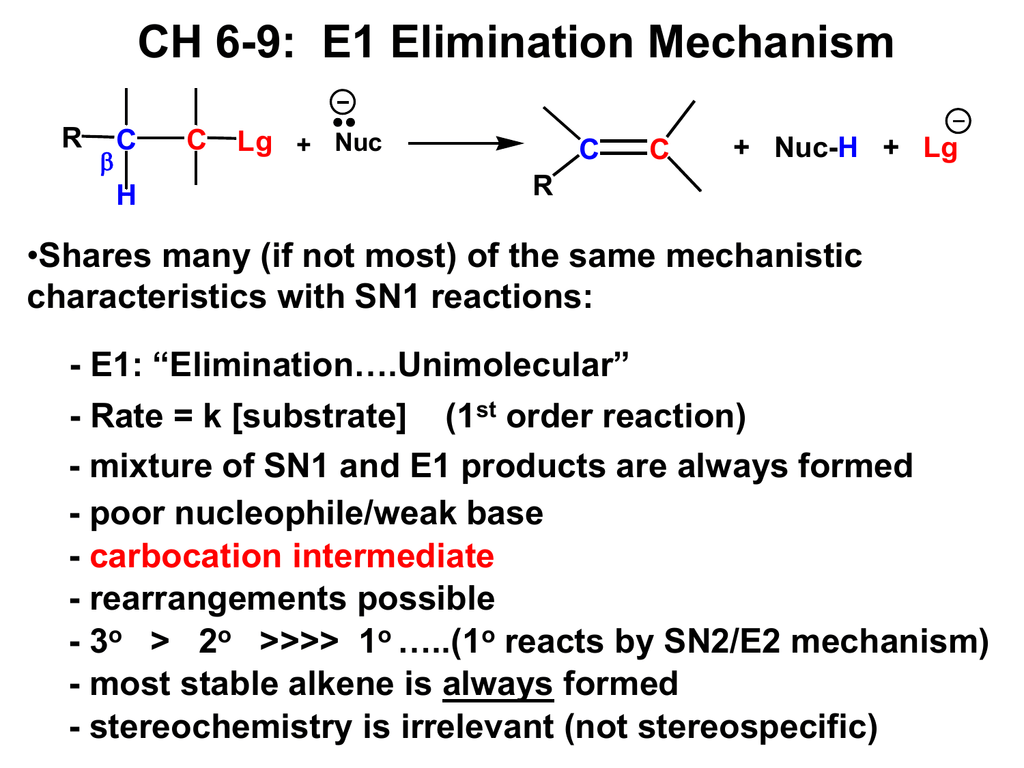
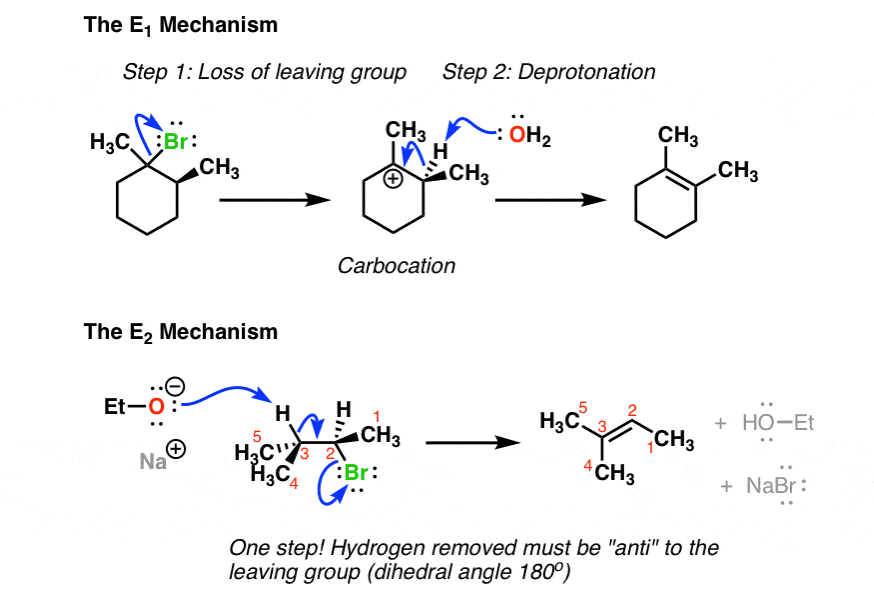
An E1 elimination begins with the departure of a leaving group (designated 'X' in the general figure above) and formation of a carbocation intermediate (step 1) Abstraction of a proton from an adjacent carbon (step 2) sends two electrons down to fill the empty p orbital of the carbocation, forming a new p bondThis video teaches you how to solve a linear system (find the point of intersection of two lines) using the algebraic method of elimination It also reviews0 @ 2 4 2 2 0 1 1 4 0 0 4 8 1 A R 3 =R 3 R 2 The original system




Troc 1 Elimination Order Youtube




Migratory Insertion 1 2 Insertions The Organometallic Reader
Products and seminars related to Elimination of Bias subject area from the The Missouri Bar Inverse of a Matrix using GaussJordan Elimination by M Bourne In this section we see how GaussJordan Elimination works using examples You can reload this page as many times as you like and get a new set of numbers each time You can also choose a different size matrix (at the bottom of the page)In mathematics, Gaussian elimination, also known as row reduction, is an algorithm for solving systems of linear equationsIt consists of a sequence of operations performed on the corresponding matrix of coefficients This method can also be used to compute the rank of a matrix, the determinant of a square matrix, and the inverse of an invertible matrix



Ch 6 9 E1 Elimination Mechanism
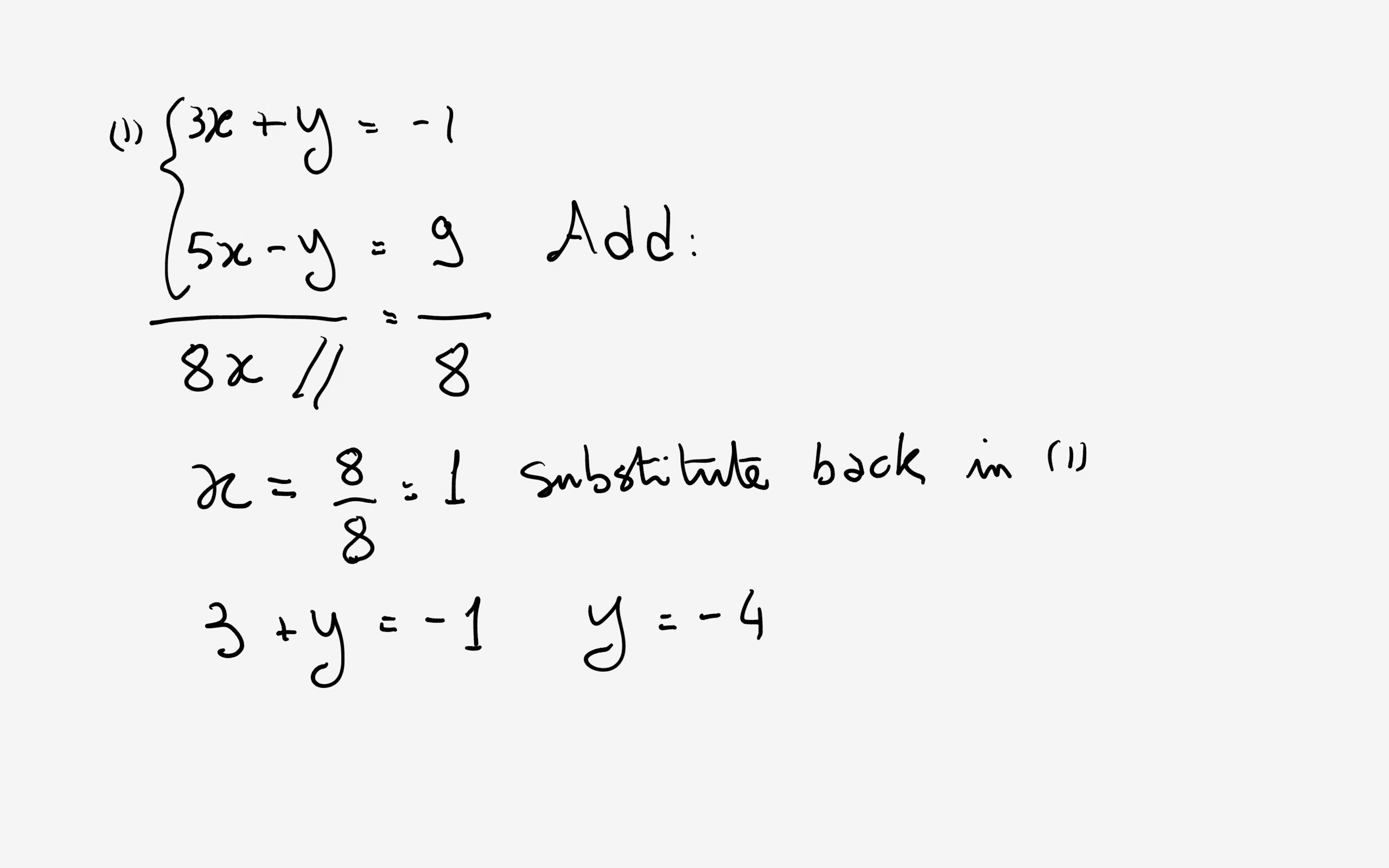



How Do You Solve The System Using The Elimination Method For 3x Y 1 And 5x Y 9 Socratic
1 Elimination = 1 SHOCK!These are the elimination method steps to solve simultaneous linear equations Let us take an example of two linear equations xy=8 and 2x3y=4 to understand it better Let, xy=8 ___ (1) and 2x3y=4 ___ (2) Step 1 To make the coefficients of x equal, multiply equation (1) by 2 and equation (2) by 1 We get,Apply gaussian elimination to column 1 of the augmented matrix, and observe that − E1 = − 4(E2 − E1) Hence = 5E1 − 4E2 Find all solutions to the following systems \arraycolsep = 1pt3x1 8x2 − 3x3 − 14x4 = 2 2x1 3x2 − x3 − 2x4 = 1 x1 − 2x2 x3 10x4 = 0 x1 5x2 − 2x3 − 12x4 = 1



1
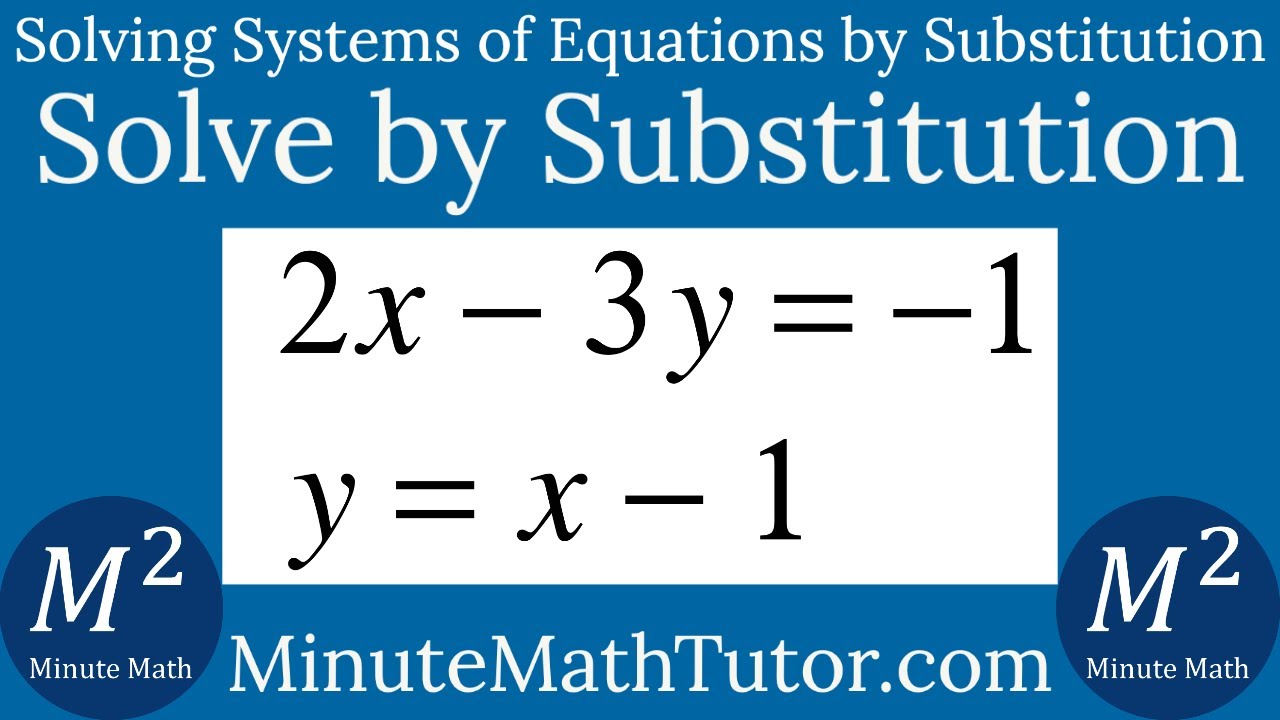



Solve 2x 3y 1 And Y X 1 By Substitution Youtube
E1 describes an elimination reaction in which the ratedetermining step is unimolecular and does not involve the base The leaving group leaves in this step, and a proton is removed in a second step This is an example of an E1 reaction which shows the formation of an alkene J F Bunnett, Angew Chemie Int Ed English, 1962, 1, 225–235An E2 elimination of 1chloro1,2diphenylethane can yield a mixture of (E) and (Z)1,2diphenylethene How would the E/Z ratio of isomers for this reaction compare to the E/Z ratio for the E2 elimination of 2bromopentane?The following steps are knows as (Gaussian) elimination They transform a system of linear equations to an equivalent upper triangular system of linear equations •Subtract l 1;0=(4=2)=2 times the first equation from the second equation Before After 2c 0 4c




Elimination Reaction Wikipedia
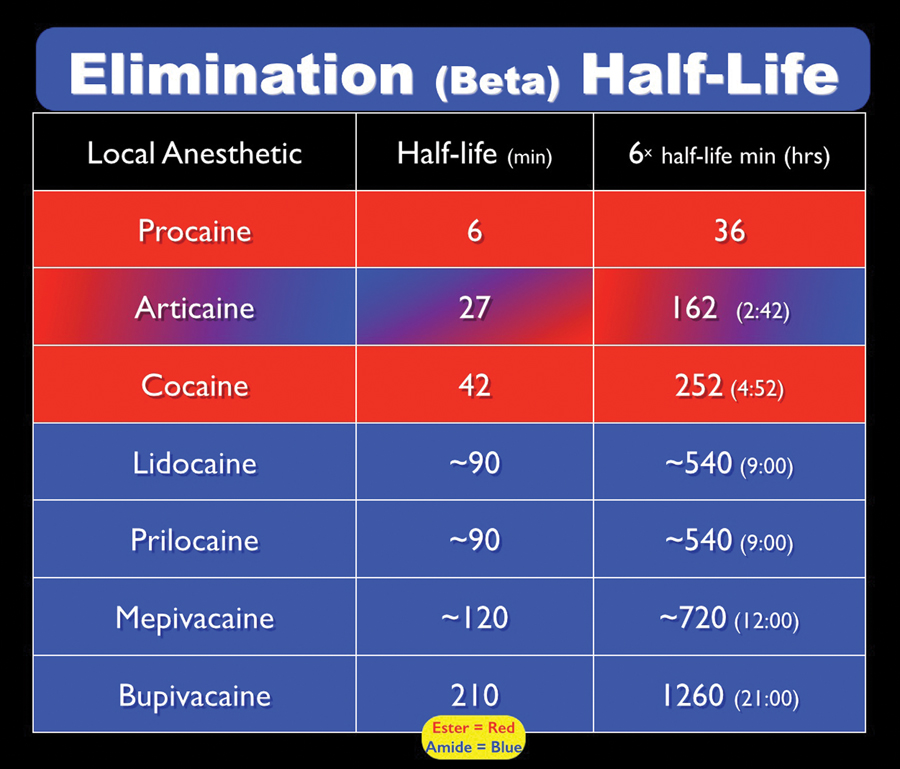



Malamed Table 1 Elimination Half Lives Of Local Anesthetics Oral Health Group
Mets Near Elimination after 51 Loss to Brewers The New York Mets are in their final 10 games of the 21 regular season schedule As of Friday, with the St Louis Cardinals winning their 14th game in a row, the Mets were officially eliminated from wildcard contention The Amazins' can be totally eliminated by the weekend1 Gaussian Elimination 11 Concepts 1In order to solve a system of equations to nd the solution or determine if there are zero or in nitely many solutions, use Gaussian elimination on the augmented matrix, a matrix formed by appending the answer vector to the original matrix A system of963 When menthyl chloride reacts with sodium ethoxide in ethanol, the only alkene product is 2menthene Explain why




Number Elimination Sesame Street Segments Wiki Fandom



1
Example 1 Solve this system Multiplying the first equation by −3 and adding the result to the second equation eliminates the variable x This final equation, −5 y = −5, immediately implies y = 1 Back‐substitution of y = 1 into the original first equation, x y = 3, yields x = 2What would be the first step in finding the solution using elimination?1 Solve LY = B by many forward substitutions (in parallel) 2 Solve UX = Y by many back substitutions (in parallel) In order to appreciate the usefulness of this approach note that the operations count for the matrix factorization is O(2 3 m 3), while that for forward and back substitution is O(m2) Example Take the matrix A = 1 1 1 2 3 5 4
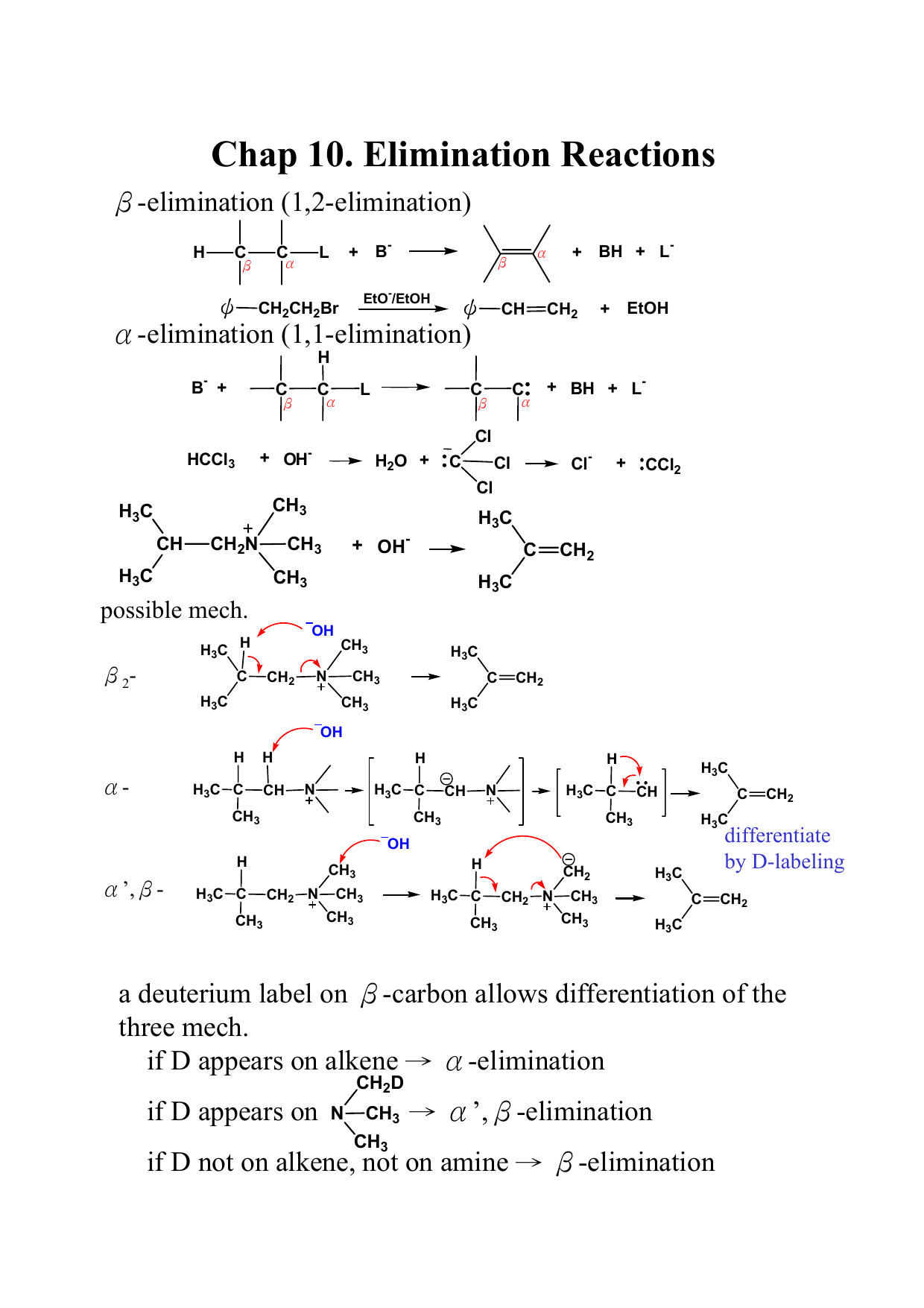



Chap 10 Elimination Reactions Elimination 1 2 Elimination B Elimination 1 1 Elimination



Elimination
SECTION 51 GAUSSIAN ELIMINATION matrix form of a system of equations The system 2x3y4z=1 5x6y7z=2 can be written as Ax ó =b ó where A= 234 567,x ó = x y z,b ó = 1 2 The system is abbreviated by writing (1) 234 567 1 2 The matrix A is called the coefficient matrixThe2Å4 matrix in (1) is called the augmented matrix and is denoted Ab GaussianElimination (of something/somebody) (from something) A 1–1 draw confirmed their elimination from the tournament uncountable (formal) the act of killing somebody, especially an enemy or opponent See elimination in the Oxford Learner's Dictionary of Academic English Check pronunciation eliminationGaussian elimination is a method of solving a system of linear equations First, the system is written in "augmented" matrix form Then, legal row operations are used to transform the matrix into a specific form that leads the student to answers for the variables Ex 3x 4y = 10 x 5y = 3




Substitution And Elimination Reaction Of Alkyl Halides By
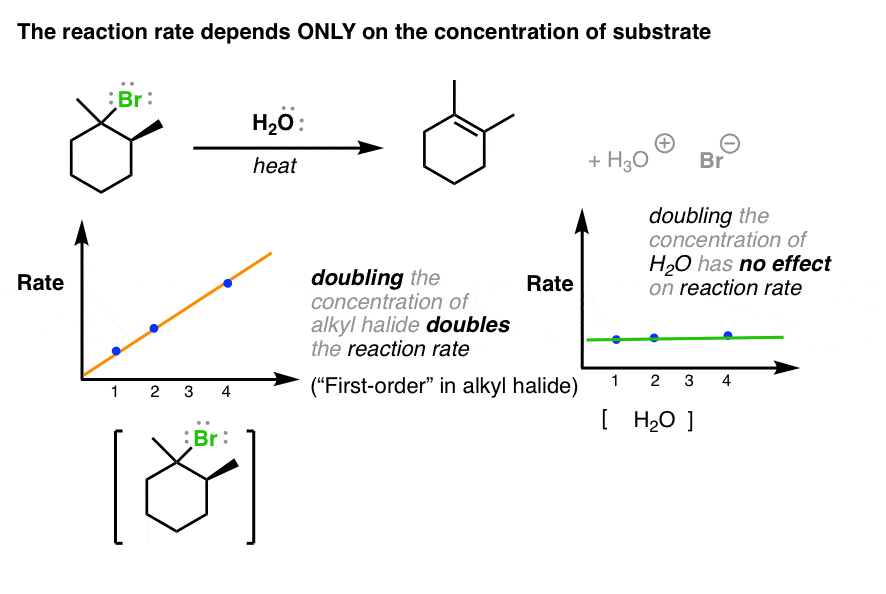



The E1 Reaction And Its Mechanism Master Organic Chemistry
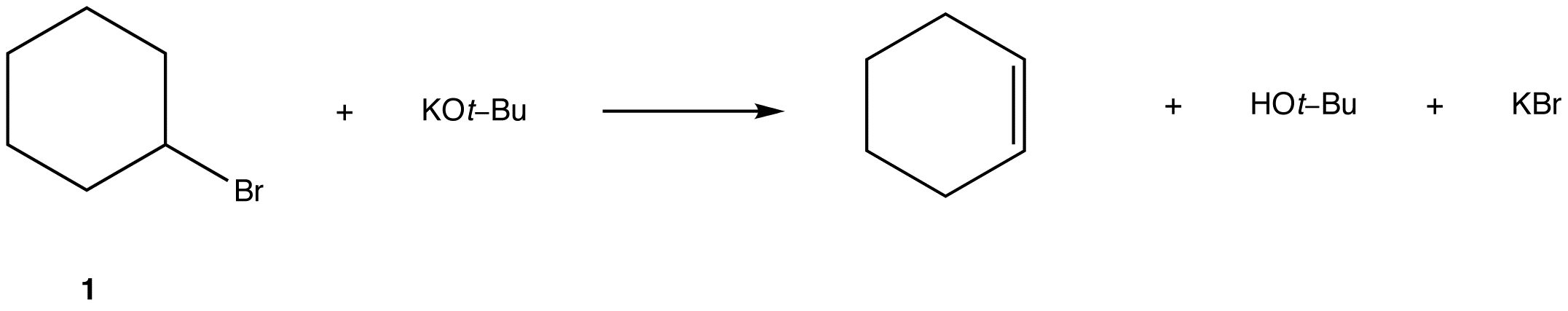
(Fortnite Troll) If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendationsChallenge 1 Running race Before the challenge was explained, Pink Car was forgotten by the host The first challenge was a running race The contestant to reach the bookmark last was eliminated However, when almost all the cars made it to the bookmark, the remaining two who haven't made it yet, Pink Car and Light Green Car, made a close finishAn example of this type of reaction in scheme 1 is the reaction of isobutylbromide with potassium ethoxide in ethanolThe reaction products are isobutene, ethanol and potassium bromide E1 mechanism E1 is a model to explain a particular type of chemical elimination reaction




Substitution Vs Elimination Predict The Outcome Labster



14 3 Elimination By The E1 Mechanism Chemistry Libretexts
Gaussian Elimination technique by matlab Learn more about ge Still not zero In fact, this one had a pretty large determinant for a known to be singular matrixCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyThis video has every elimination from Total Drama Island to Total Drama All Stars I don't own aything All credit to Google Images and the people who brings
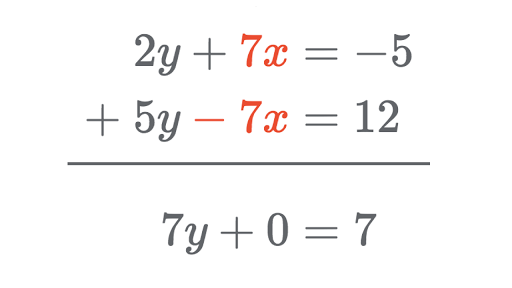



Elimination Method Review Systems Of Linear Equations Article Khan Academy



1 2 Elimination Chemistry Libretexts
1 2 14 The Method of Elimination • MHR 37 Example 3 Find a Point of Intersection Using Elimination Find the point of intersection of the linear system 4x 3y 13 5x 4y 7 Verify your answer Solution 4x 3y 13 5x 4y 7 Method 1 Eliminate x 5 x 15y 65 4 x 16y 28 31y 93 y y 3 Substitute y 3 into to find the corresponding xvalue 4x 3y 13 4x2x 2y = 2 3x 2y = 12 answer choices you cannot solve this using elimination cross out the 2x and 3x Add the like terms The y terms will zero out change to slope intercept form and graph0 @ 2 4 2 2 0 1 1 4 0 1 5 12 1 A R 2 =R 2 2R 1 R 3 =R 3 R 1!




8 2 E1 Reaction Organic Chemistry



11 10 The E2 Reaction And Cyclohexane Conformation Chemistry Libretexts
Elimination reaction 1 Elimination Reaction Elimination reactions involve the loss of elements from the starting material to form a new π bond in the product Alkyl halides (RX) undergo elimination with bronsted bases The elements of HX are lost and alkene are formedThe main features of the E1 elimination are It usually uses a weak base (often ROH) with an alkyl halide, or it uses an alcohol in the presence of H 2 SO 4 or H 3 PO 4 Only secondary or tertiary alkyl halides are effective reactants, with tertiary reacting most easily Heat is often used to minimize competition from S N 1Gaussian elimination (also known as Gauss elimination) is a commonly used method for solving systems of linear equations with the form of K {u} = {F} In matrix operations, there are three common types of manipulation that serve to produce a new matrix that possesses the same characteristics as the original 1 Interchange any two rows 2




Elimination Reaction Wikipedia




Difference Between Alpha And Beta Elimination Reaction Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Ax 3y = —3 4x 6y = 6 he3 Z3 oyz _____ 1ane4)7 I IT k s c'owii r ' 2i bi 4i# 3 Elimination with three Equations and Three Unknowns The methodology we used for the two equations with two unknowns sit uation works for three equations with three unknowns, or in general for nM7 GaussJordan Elimination GaussJordan Elimination is an algorithm that can be used to solve systems of linear equations and to find the inverse of any invertible matrix It relies upon three elementary row operations one can use on a matrix Swap the positions of two of the rows Multiply one of the rows by a nonzero scalarExampleFor which numbers a does elimination break down (1) per manently (2) temporarily?




Homework 3 Answers Chemistry




Elimination Reaction
Each leading 1 of a row is to the right of the leading 1 of the row above All zero rows are at the bottom And there you have it, we are finally ready to do the Gaussian Elimination! 1 A (1) We apply Gaussian elimination To keep track of the operations, we use, eg, R 2 =R 2 2R 1, which means that the new row 2 is computed by subtracting 2 times row 1 from row 2 0 @ 2 4 2 2 4 9 3 8 2 3 7 10 1 A!




Systems Of Equations With Elimination 3t 4g 6 6t G 6 Video Khan Academy




Elimination Reaction Wikipedia




Elimination Reaction Definition Examples Mechanism And Applications



1



Elimination Pd2 Math 15 16
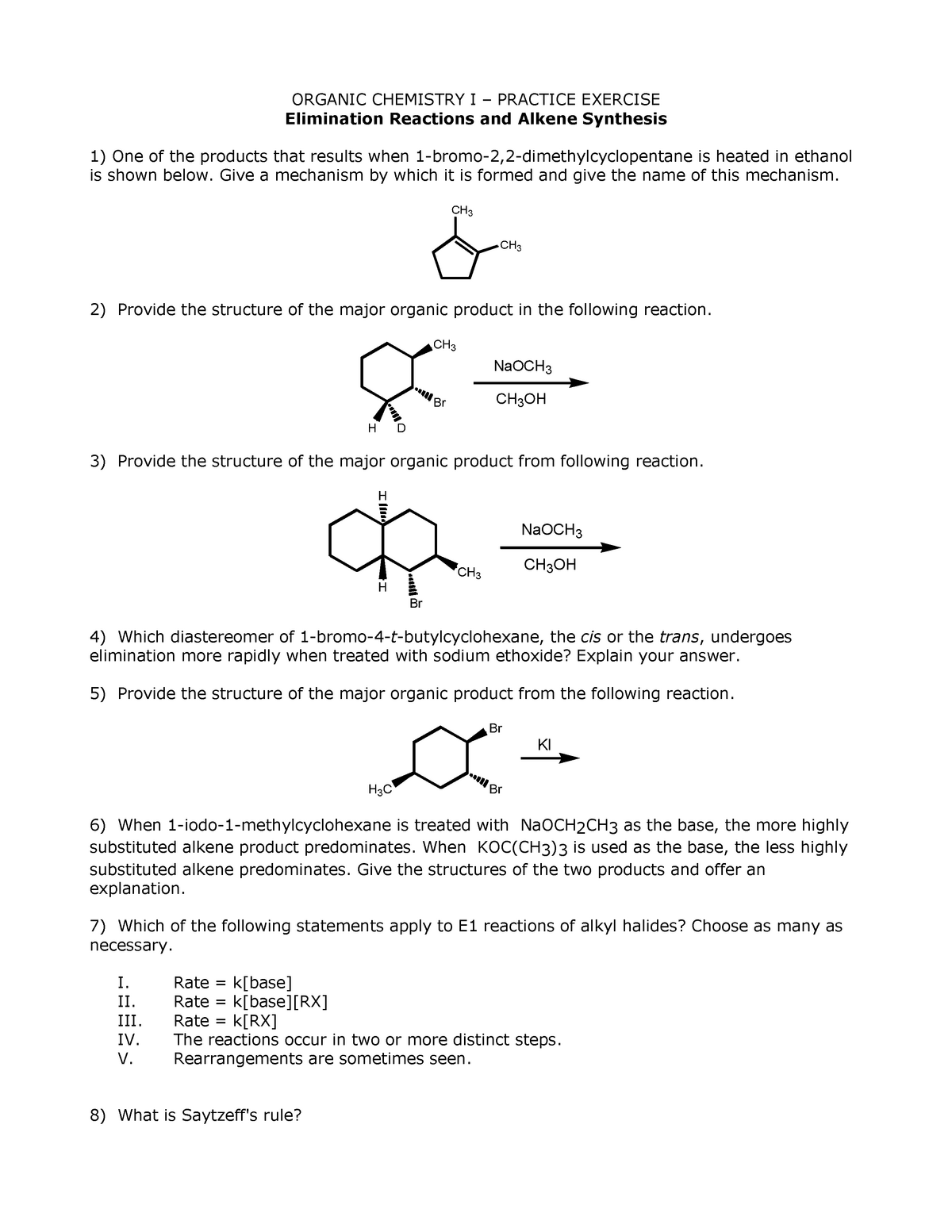



Elimination Reactions Alkene Synthesis Worksheet With Answer Key Organic Chemistry I Practice Studocu



Elimination 1 Resident Evil Wiki Fandom
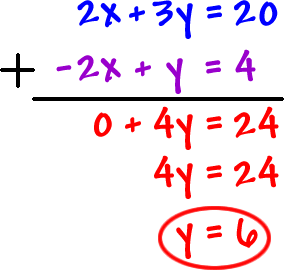



Solving By Elimination 1
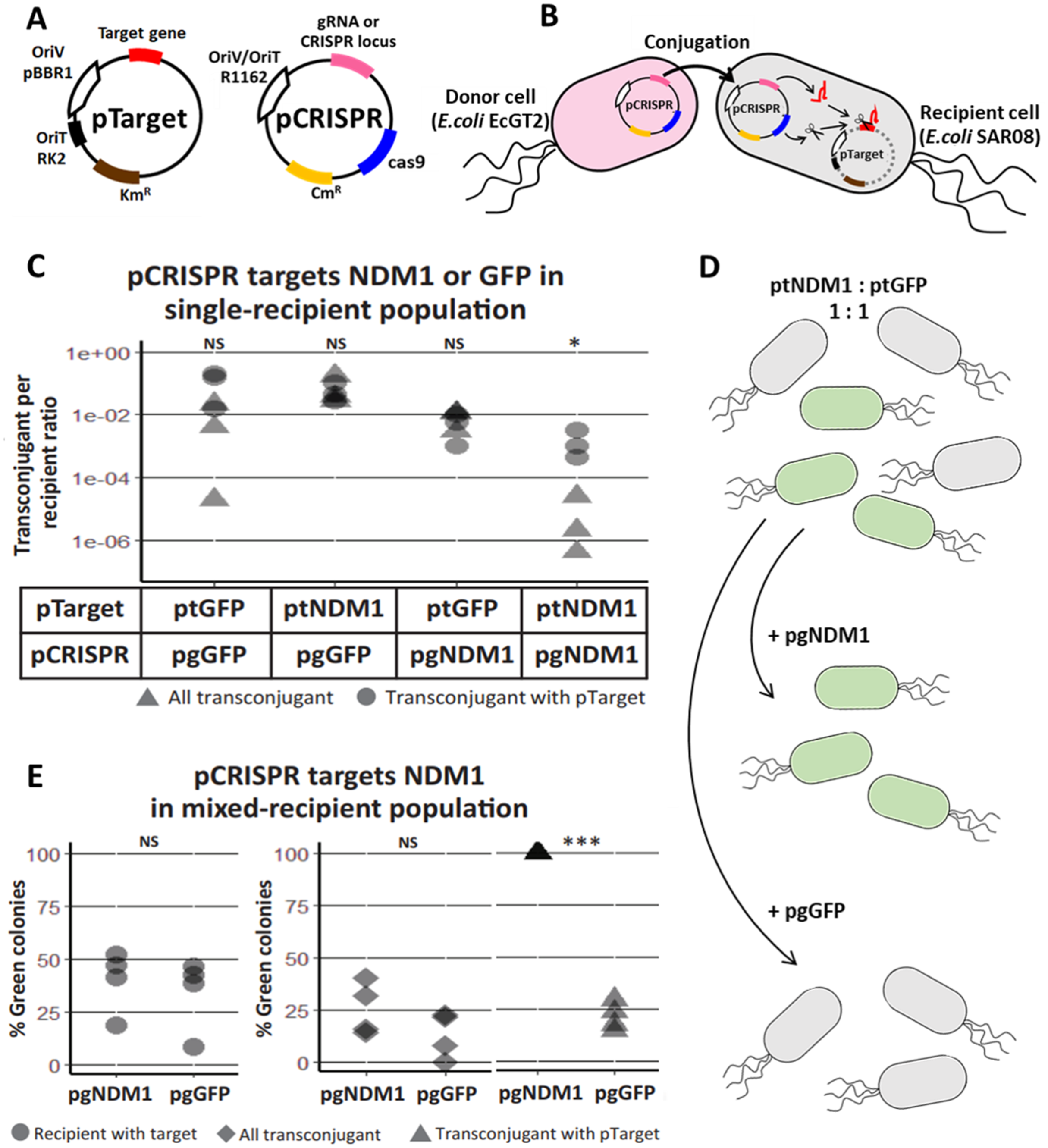



A Highly Effective And Self Transmissible Crispr Antimicrobial For Elimination Of Target Plasmids Without Antibiotic Selection Peerj




Elimination Reaction Wikipedia




Elimination Reactions Chapter 6 1 Elimination Reactions W




8 5 Elimination Reactions Organic Chemistry 1 An Open Textbook




Solution Draw The Product Of The E2 Elim Organic Chem




1 1 1 2 And 1 4 Eliminations From The Corresponding Dihalogenated Compounds Using Bu3snsime3 F Sciencedirect




E1 Reaction Mechanism And E1 Practice Problems
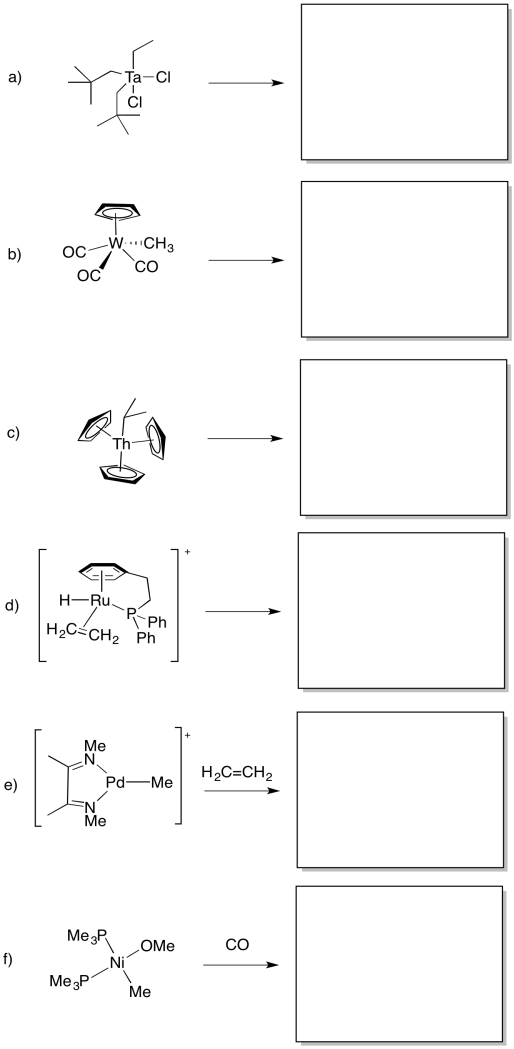



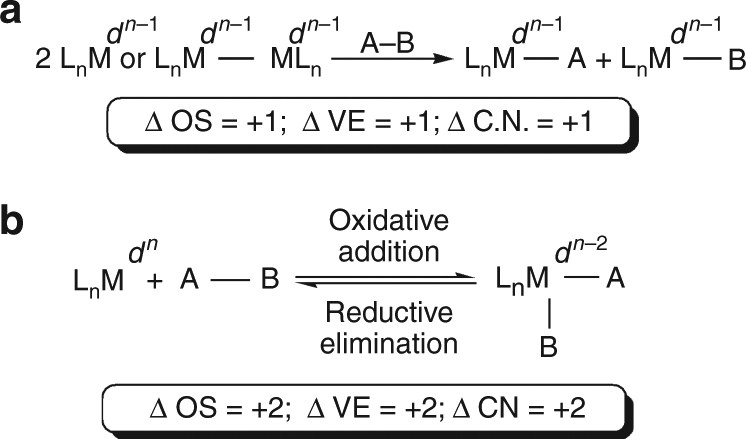
Organometallic Insertion




How To Solve Linear Systems Using Gaussian Elimination Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Targeted Elimination Of Senescent Beta Cells Prevents Type 1 Diabetes Sciencedirect
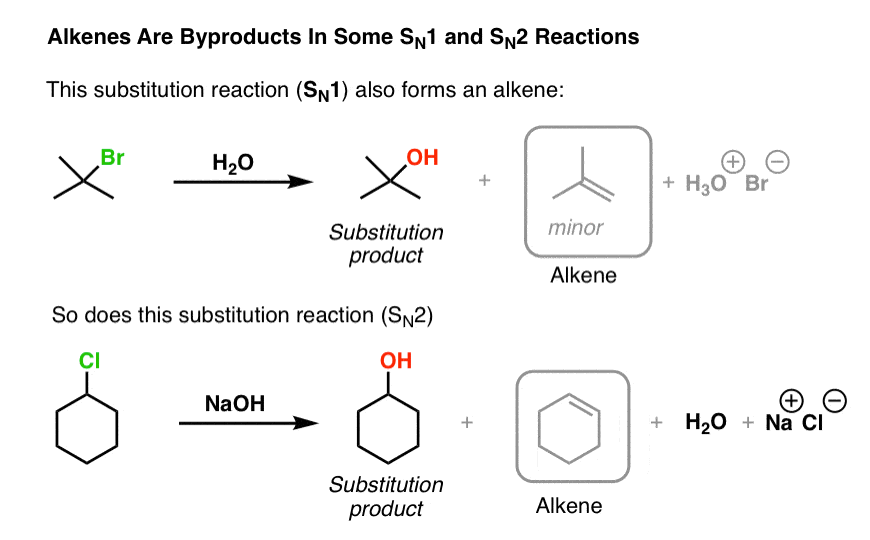



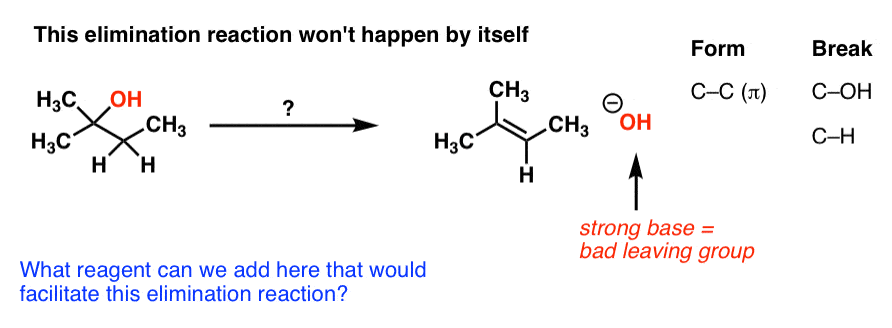
Introduction To Elimination Reactions The Key Pattern
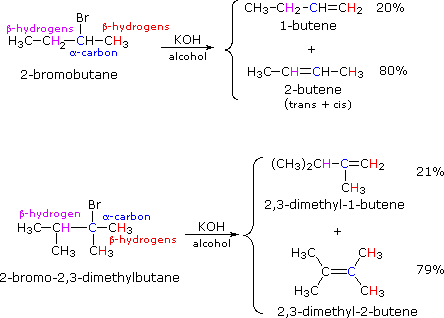



Alkyl Halide Reactivity



Evidence For Single Metal Two Electron Oxidative Addition And Reductive Elimination At Uranium Nature Communications




Coupling Of The Staudinger Reduction And 1 6 Elimination For The Download Scientific Diagram




E2 Elimination An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Substitution And Elimination Reaction Of Alkyl Halides By
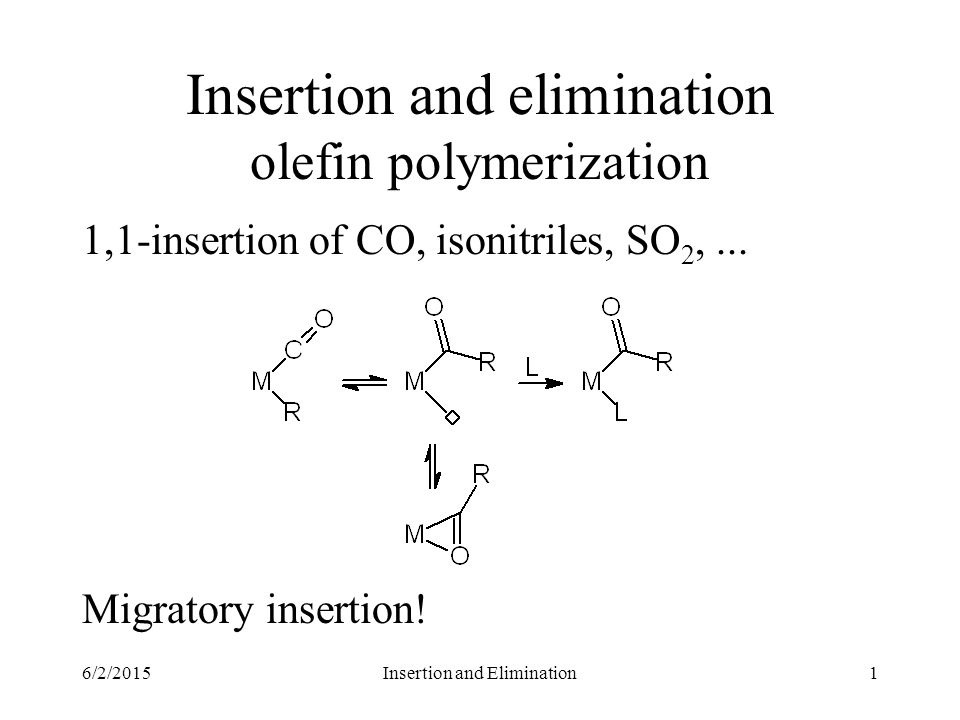



Insertion And Elimination Olefin Polymerization Ppt Video Online Download




Commemorating The 74th Anniversary Of The First Un Resolution 1 1 Elimination Of Nuclear Weapons Unfold Zero




Solving A System Of Equations With Elimination Kate S Math Lessons
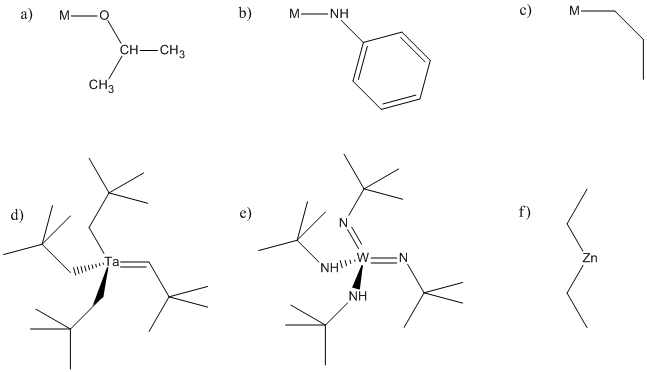



Organometallic Insertion




Elimination Reactions Online Organic Chemistry Tutor
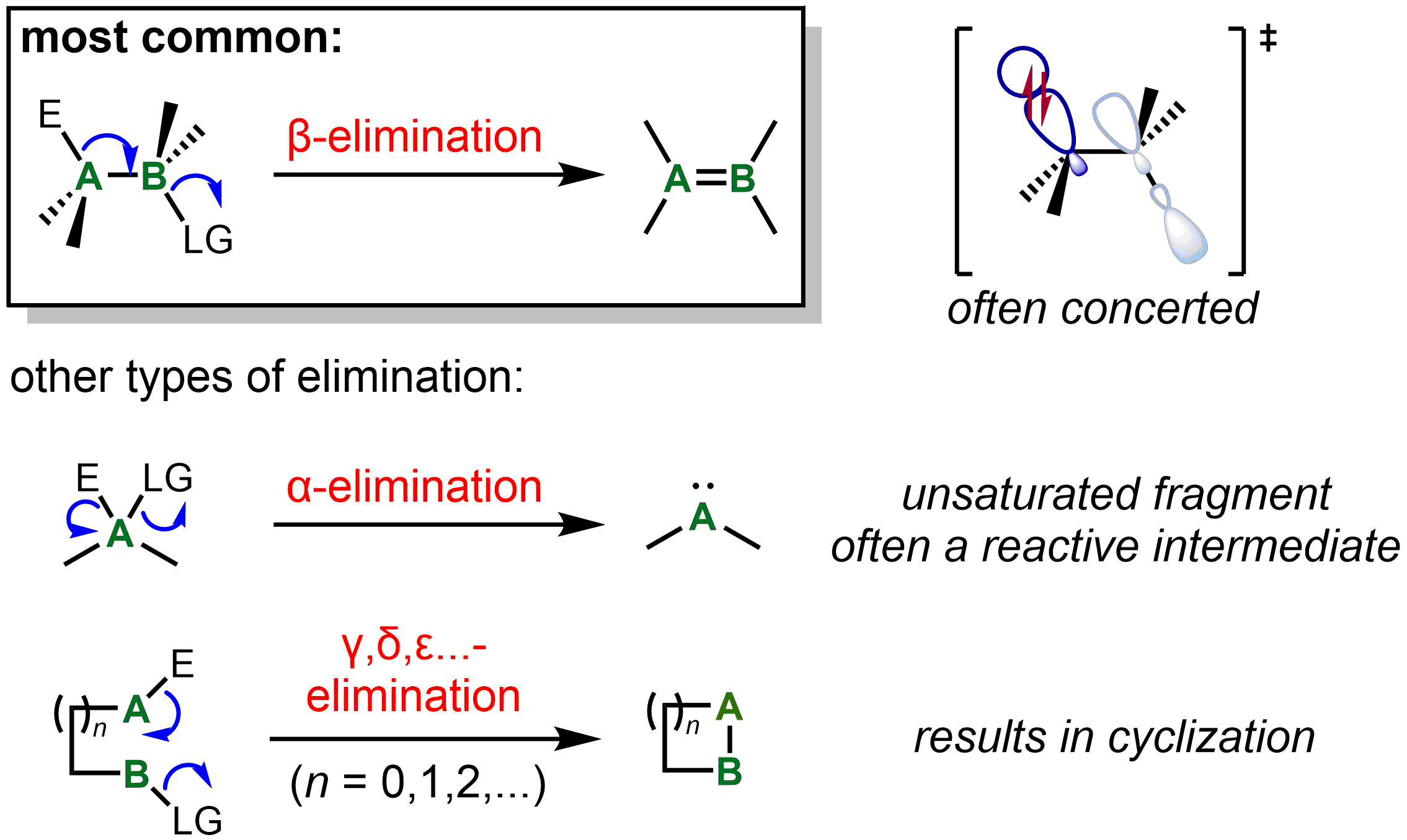



Elimination Reaction Wikiwand




Elimination Reaction Definition Examples Mechanism And Applications



Cyclodes



2




7 8 Case Study Gaussian Elimination



Alkyl Halide Reactivity




8 1 Point Consider The Following Gauss Elimination 10 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 Homeworklib




Camp Battle Royale Season 1 Elimination Order By Objectdudeisland On Deviantart



Comparing The E1 Vs Sn1 Reactions Master Organic Chemistry




8 5 Elimination Reactions Organic Chemistry 1 An Open Textbook
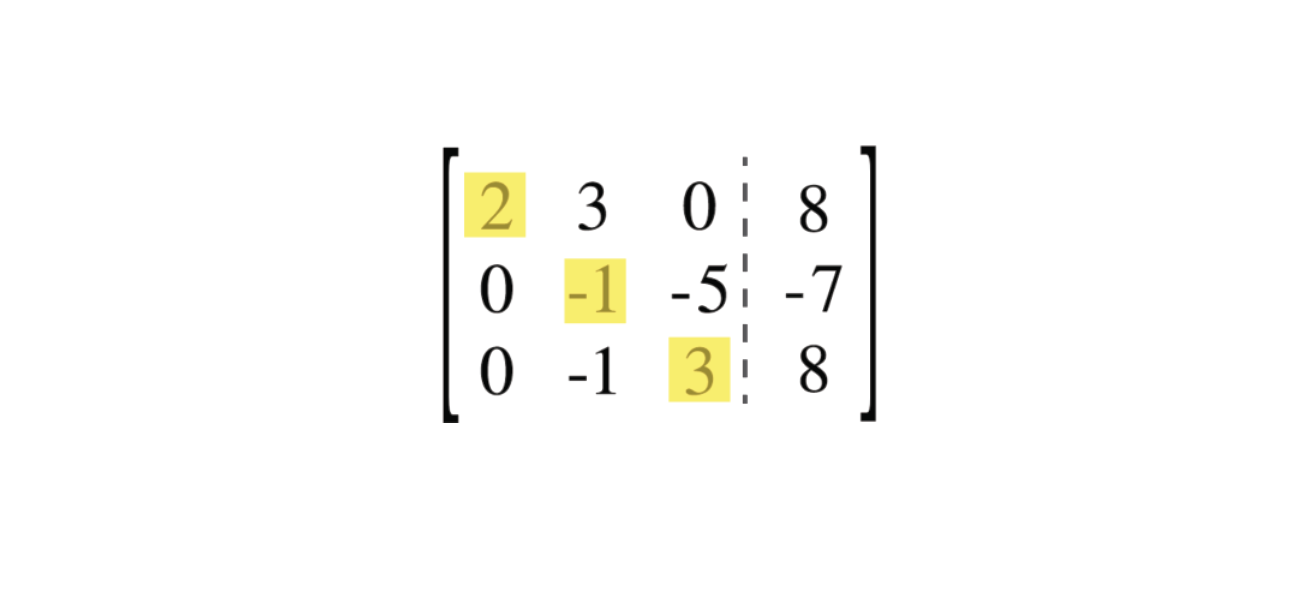



1 3 A Complete Guide To Gaussian Elimination By Adam Dhalla Medium
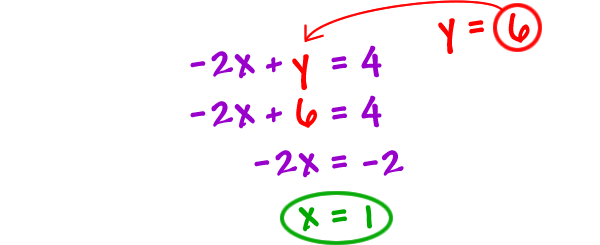



Solving By Elimination 1



Reaction D Elimination E1 Et E2 Pdf



E1 Vs E2 Comparing The E1 And E2 Reactions Master Organic Chemistry




Gaussian Elimination Numerical Methods



A Complete Guide To Gaussian Elimination By Adam Dhalla Artificial Intelligence In Plain English




Introduction To Elimination Reactions Youtube




Is The Elimination Reaction Between 1 1 Dibromo Cyclopropane And Phenyl Lithium Feasible In Alkaline Medium And Some Heat Chemistry Stack Exchange




Stereoselectivity Of E2 Elimination Reactions




1 1 Elimination Chemistry Libretexts
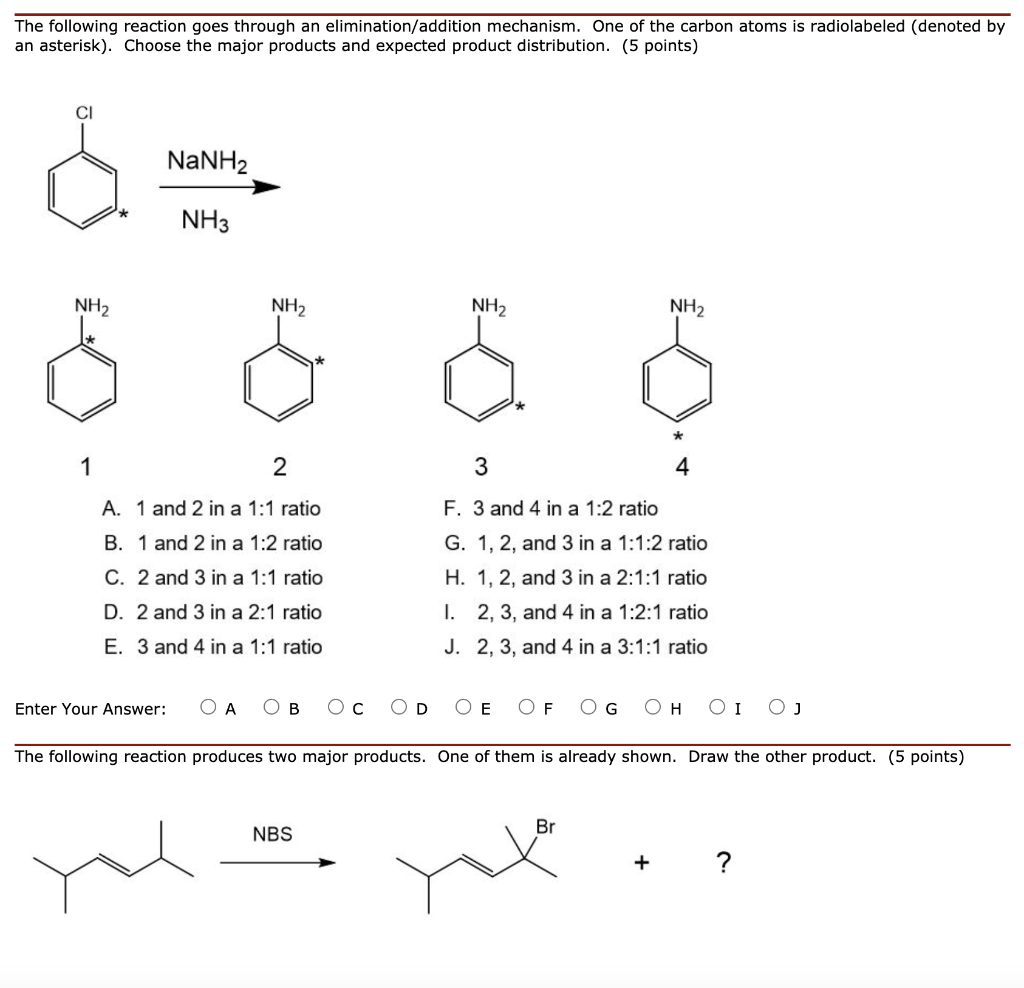



Solved The Following Reaction Goes Through An Chegg Com




8 5 Elimination Reactions Organic Chemistry 1 An Open Textbook
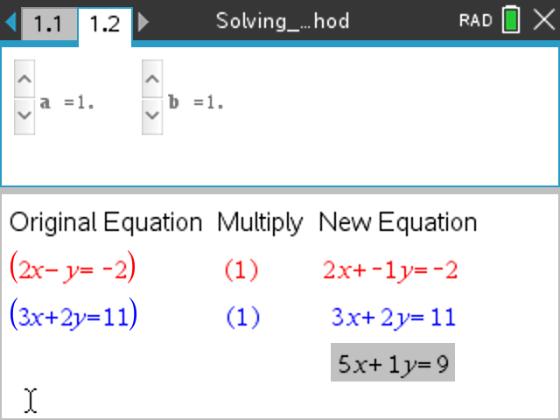



Algebra 1 Solving Systems By The Elimination Method Algebra I Ti Math Nspired




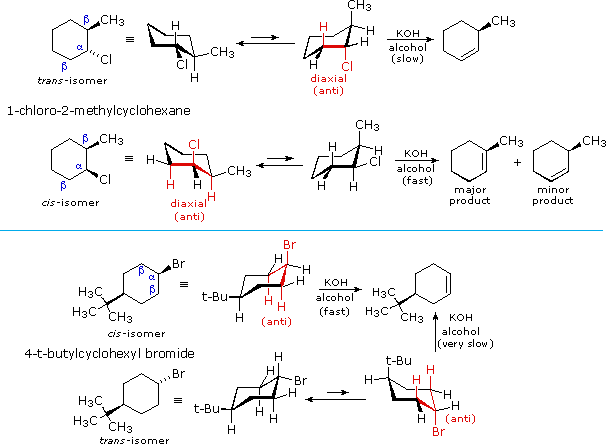
Elimination Reaction With 1 2 Dibromo 4 Methylcyclohexane Chemistry Stack Exchange




Holt Algebra Solving Systems By Elimination 6 3 Solving Systems By Elimination Holt Algebra 1 Warm Up Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Presentation Ppt Download




Elimination Diet Meal Plan 1 Week 1 Person Papillon Foods




Activation Mechanisms Of Self Immolative Linkers A 1 6 Elimination Download Scientific Diagram
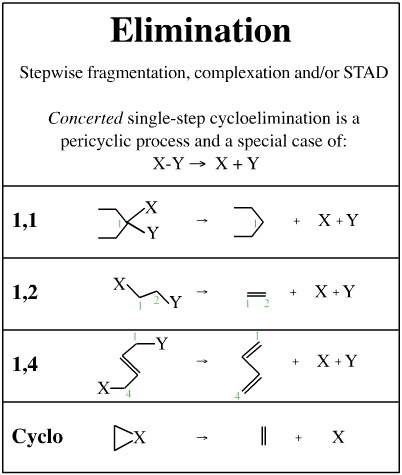



Unit Compound Mechanistic Steps Chemogenesis




Elimination Reaction E1 E2 Reaction Mechanisms




Elimination Diet Meal Plan 1 Week 1 Person Papillon Foods
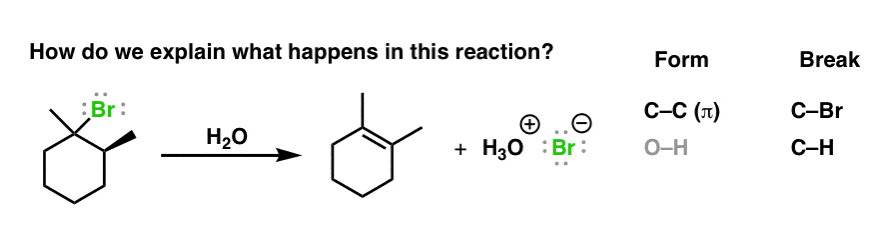



The E1 Reaction And Its Mechanism Master Organic Chemistry




Elimination Diet Resources Whole Life Nutrition



1 1 Elimination Ochempal




Phase 1 Elimination Diet Recipes Elimination Diet Recipes Elimination Diet Elimination Diet Meal Plan




Following Compounds Are Given To You 2 Bromopentane 2 Bromo 2 Methylbutane 1 Bromopentane I Write The Compound Which Is Most Reactive Towards S N 2 Reaction Ii Write The Compound Which Is Optically Active Iii Write



1
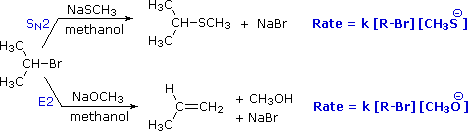



Alkyl Halide Reactivity




The Impact Of Social Protection And Poverty Elimination On Global Tuberculosis Incidence A Statistical Modelling Analysis Of Sustainable Development Goal 1 The Lancet Global Health
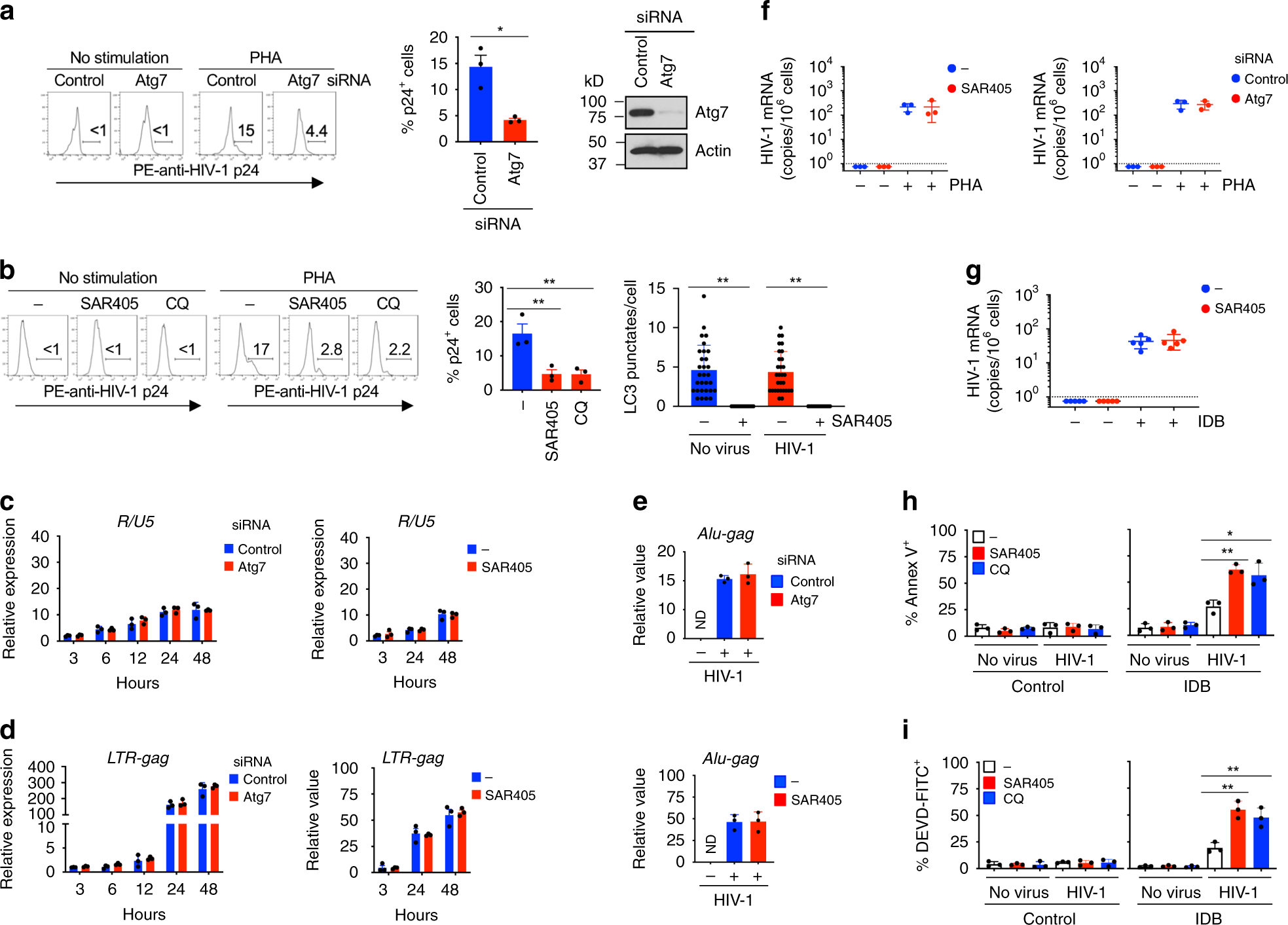



Clearance Of Hiv Infection By Selective Elimination Of Host Cells Capable Of Producing Hiv Nature Communications




Fortran Gaussian Elimination Code Unclear Askprogramming
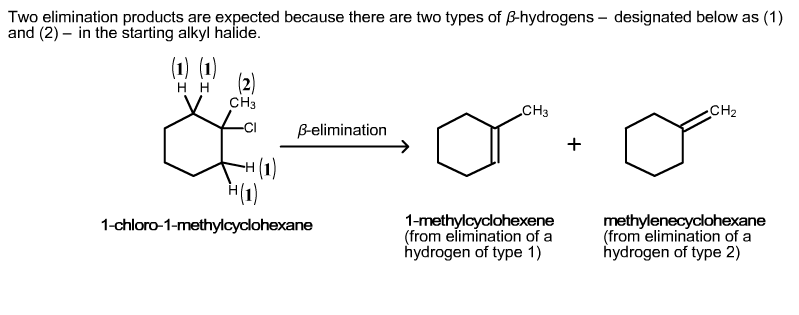



Solved Two Elimination Products Are Expected Because There Chegg Com



2




Naive Gauss Elimination Matlab Quesion Stack Overflow




The Camp Of Kewlness Season 1 Elimination Order By Azoicassaultaids On Deviantart



2
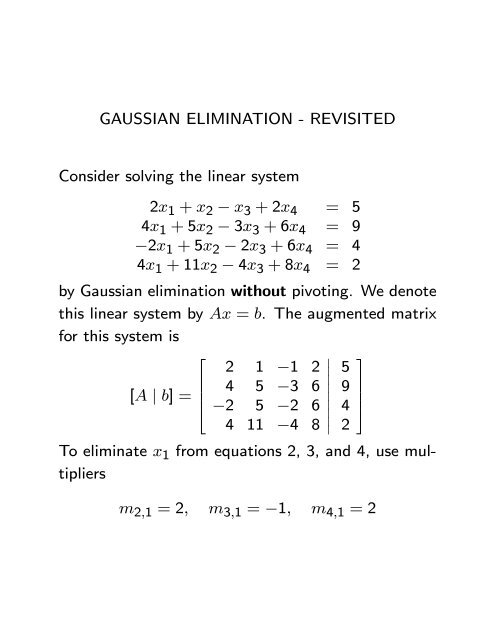



Gaussian Elimination Revisited Consider Solving The Linear




Solved Problem Solving Classify The Following Reactions As Chegg Com




What Product S Are Expected In The Ethoxi Clutch Prep




Strainz 1 Elimination Appid Steamdb
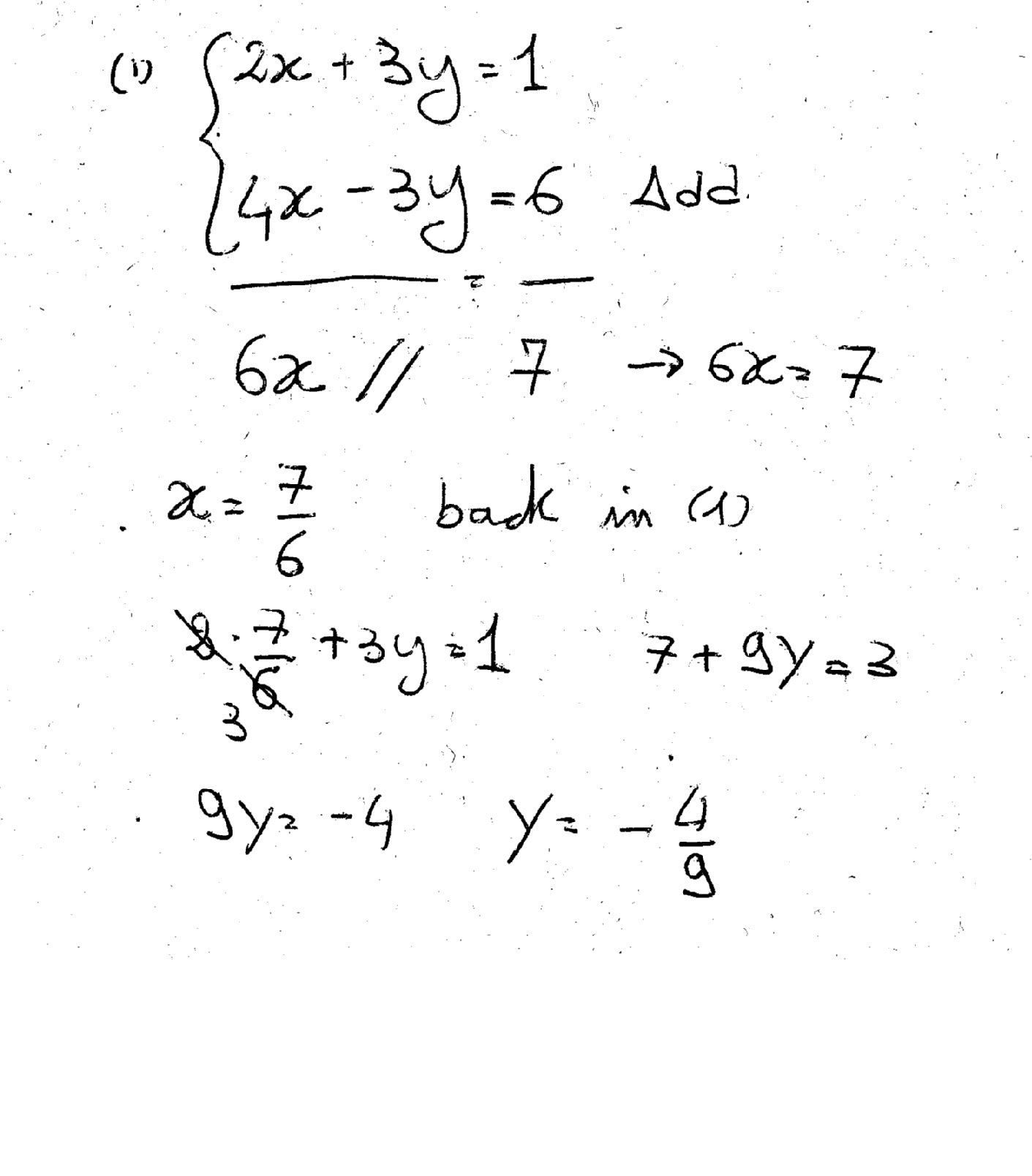



How Do You Solve The System Using The Elimination Method For 2x 3y 1 And 4x 3y 6 Socratic




Algebra 1 Common Core Elimination By Multiplication Ks Ia1



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿